
The concept of the Global South goes beyond a mere geographical division and is used to highlight issues related to development, geopolitics, and global inequalities. Read here to learn more about the significance of the grouping.
Recently, India hosted the 2nd Voice of the Global South Summit in virtual mode. The 2nd summit focussed on sharing with countries of the Global South the key outcomes achieved in various G20 meetings throughout India’s Presidency.
The VoGS Summit is an Indian initiative that has been designed to provide a common platform for the countries of the Global South to share their perspectives and priorities on several major issues.
It aims to find solutions for common challenges faced by developing countries through talks.
Global south

The term “Global South” refers to a grouping of countries or regions located primarily in the southern hemisphere, which are often characterized by lower income levels, less industrialization, and different social, political, and economic challenges compared to the more economically developed countries in the northern hemisphere, often referred to as the “Global North.”
The considerations related to the Global South that make them a grouping are:
- Economic Disparities: Countries in the Global South generally face economic challenges, including lower per capita income, higher levels of poverty, and limited access to resources. Many of these nations rely heavily on agriculture, and there may be a lack of economic diversification.
- Development Challenges: The Global South is often characterized by challenges related to development, including inadequate infrastructure, healthcare, and education. Access to basic services and social development indicators may be lower compared to the Global North.
- Globalization and Dependency: The Global South is often seen as having a history of being economically and politically dependent on the Global North. This dependency can manifest through trade relationships, international debt, and global economic structures.
- Colonial Legacy: The historical legacy of colonization has had a lasting impact on many countries in the Global South. Former colonies often continue to grapple with the social, economic, and political consequences of colonial rule.
- Cultural Diversity: The Global South is culturally diverse, with a rich tapestry of languages, religions, traditions, and ethnicities. This diversity is often a source of strength and resilience for these regions.
- Geopolitical Considerations: The term Global South is also used in geopolitical discussions to refer to a bloc of nations that often share common positions on issues such as trade, climate change, and development assistance in international forums.
- Global South-South Cooperation: Some countries in the Global South have engaged in South-South cooperation, a form of collaboration where developing nations work together to address common challenges. This cooperation involves the exchange of resources, knowledge, and technology among countries in the southern hemisphere.
- Challenges and Opportunities: While the Global South faces numerous challenges, there are also opportunities for growth and development. Some nations in these regions have experienced economic success, improved social indicators, and increased influence on the global stage.
- Environmental Issues: The Global South is often disproportionately affected by environmental challenges, including climate change, deforestation, and loss of biodiversity. These issues can have severe consequences for communities that are heavily dependent on natural resources.
- Rising Influence: In recent years, some countries in the Global South, particularly in Asia, have experienced rapid economic growth and increased geopolitical influence. This has led to shifts in the global balance of power.
History of Global South
Global South is intertwined with the broader historical processes of colonialism, decolonization, economic development, and global power dynamics.
Colonial Era (15th–20th centuries): The colonial era marked a period of European exploration, conquest, and colonization, during which European powers established empires in Africa, Asia, and the Americas.
- The exploitation of resources forced labor, and the imposition of European cultural and political systems had lasting impacts on the societies of the colonized regions.
Decolonization (mid-20th century): After World War II, a wave of decolonization occurred as former colonies sought independence. Many countries in Africa and Asia gained sovereignty from European colonial powers.
- The process of decolonization led to the establishment of new nation-states but also left challenges, such as artificial borders, economic dependence, and social divisions.
Cold War Era (1945–1991): The Cold War rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union influenced global politics. Some newly independent nations in the Global South aligned with one of the superpowers or pursued non-alignment.
- Cold War dynamics contributed to geopolitical interventions and conflicts in the Global South, often exacerbating existing challenges.
Development and Economic Challenges: Many countries in the Global South faced economic challenges, including a legacy of underdevelopment, dependence on commodity exports, and debt burdens. Efforts to achieve economic development and reduce poverty became central concerns.
Non-Aligned Movement (1961): The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) was founded by newly independent countries seeking to remain neutral in the Cold War. The movement aimed to promote economic development, sovereignty, and international cooperation among nations of the Global South.
Globalization and Economic Shifts (late 20th century): The latter half of the 20th century saw increased globalization, with economic changes impacting countries in the Global South. Structural adjustment programs, trade liberalization, and globalization had mixed effects on different nations.
Rise of Emerging Economies (21st century): In the 21st century, certain countries in the Global South, often referred to as emerging economies, experienced rapid economic growth. China, India, Brazil, and others became influential players in the global economy.
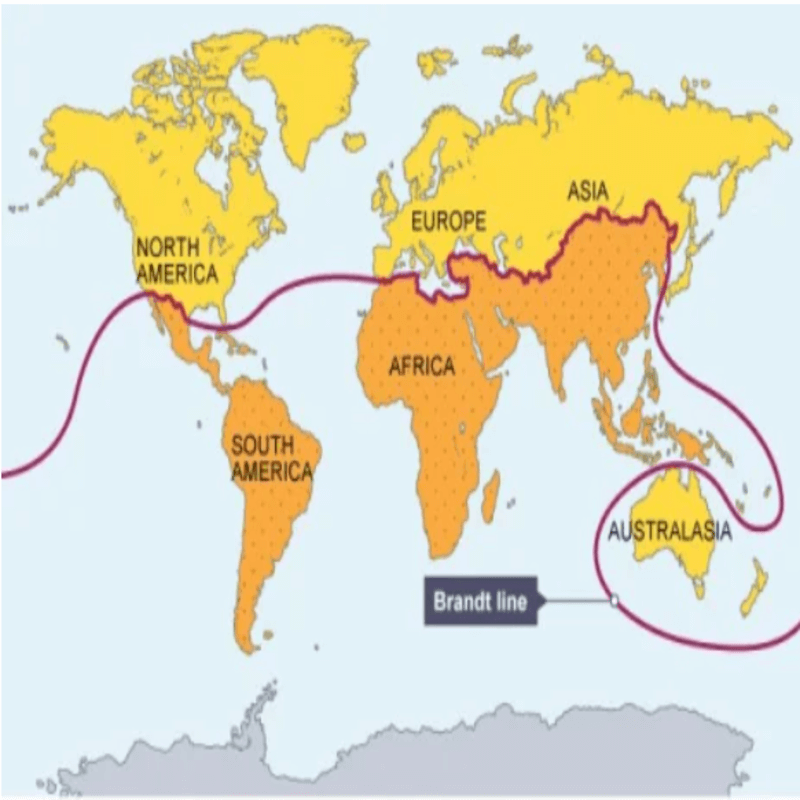
Brandt line
The Brandt Line refers to an imaginary division of the world into the “North” and the “South” based on economic disparities and development indicators. It was proposed by the German statesman and former Chancellor, Willy Brandt, in the 1980s. The Brandt Line is a visual representation of the economic and developmental divide between the more developed and less developed regions of the world.
G77
The Group of 77 (G77) is a coalition of developing nations that was established on June 15, 1964.
- The G77 was formed during the first session of the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) held in Geneva in 1964.
The group was formed within the United Nations to promote the collective economic interests of its member countries and to enhance their negotiating capacity on various international issues.
The G77 has since expanded its membership and plays a significant role in global diplomatic and economic forums.
Objectives: The primary objectives of the G77 are to promote economic cooperation among its member countries, strengthen their negotiating capacity in international forums, and advocate for their common interests, particularly in the context of international economic and development issues.
Global South Representation: The G77 represents the interests of developing countries, often referred to as the “Global South.” Member countries span various regions, including Africa, Asia, Latin America, and the Middle East.
Cooperation and Solidarity: The G77 emphasizes cooperation and solidarity among developing nations. It provides a platform for member countries to collaborate on issues such as trade, development assistance, climate change, and international economic policies.
United Nations System: The G77 operates within the United Nations system and is actively involved in UN processes, negotiations, and conferences. It works to amplify the voices of developing nations and seeks to influence international policies to address the needs and concerns of its members.
South-South Cooperation: The G77 promotes South-South cooperation, which involves collaboration among countries in the Global South to share resources, knowledge, and technology for mutual development. This approach is seen as an alternative to traditional North-South development models.
Annual Chairmanship: The G77 operates on a system of annual chairmanship. The chairmanship rotates among the regional groups represented in the G77, allowing different regions to lead the group and advocate for their specific concerns.
Group of 24 (G24): The G77 is often associated with the Group of 24 (G24), which is a subgroup that focuses on international monetary and financial issues. The G24 represents the interests of developing countries in discussions with institutions such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank.
The G77 plays a crucial role in advocating for the interests of developing nations on issues such as trade, debt relief, climate change, sustainable development, and the reform of international institutions.
Conclusion
It’s important to note that the terms “Global South” and “Global North” are generalizations, and there is considerable diversity within each grouping. Additionally, the terms themselves can be contested, and some argue that they oversimplify complex global dynamics. Nevertheless, the concepts are often used in discussions of global development, international relations, and social justice.
-Article by Swathi Satish






Leave a Reply