On earth, there are five major types of biomes: aquatic, grassland, forest, desert, and tundra.
Grasslands account for up to 40% of the Earth’s land surface.
Grasslands usually lie between deserts and mountain climates.
There are two types of grasslands; tropical and temperate.
However, only about 10% of world’s grass lands are protected.
Grasslands in news
Recently, Prime Minister of India, Narendra Modi, reintroduced Cheetah to Kuno Palpur National Park which is translocated from the African country Namibia.
Do you know why cheetah and Grasslands are related?
The reason for choosing cheetah was based on the conservation benefits.
Cheetah is a grassland-based species.
Grasslands have reduced drastically in India.
Grassland-based fauna has declined.
In saving the cheetah other species which are grassland based and endangered are also saved.
Grasslands, will also, get conserved.
What are grasslands?
UNESCO defines grassland as “land covered with herbaceous plants with less than 10 per cent tree and shrub cover” and wooded grassland as 10-40 per cent shrub cover.
Grasslands are also called transitional landscapes. In this ecosystem, the vegetation is dominated by herbs and grass.
These ecosystems are mainly found in regions, where there is a scarcity of water and not enough regular rainfall to support the growth of plants and forests.
The grassland ecosystem lies between the deserts and the forest ecosystems.
Savanna grasslands and temperate grasslands are some examples of grassland ecosystems.
Grasslands are one of the intermediate stages in ecological succession and cover a part of the land at all altitudes and latitudes at which climatic and soil conditions do not allow the growth of trees.
This ecosystem makes up almost a quarter of the total land surface and covers areas where rainfall is usually low and/or the soil depth and quality are poor.
The low rainfall prevents the growth of numerous trees and shrubs but is sufficient to support the growth of grass cover during the monsoon.
Where grasslands are found?
Grassland occurs where there is sufficient moisture for grass growth, but where environmental conditions, both climatic and anthropogenic prevent tree growth.
Its occurrence, therefore, correlates with a rainfall intensity between that of desert and forest and is extended by grazing or fire to form a plagioclimax in many areas that were previously forested.
These ecosystems are particularly fragile because water is scarce.
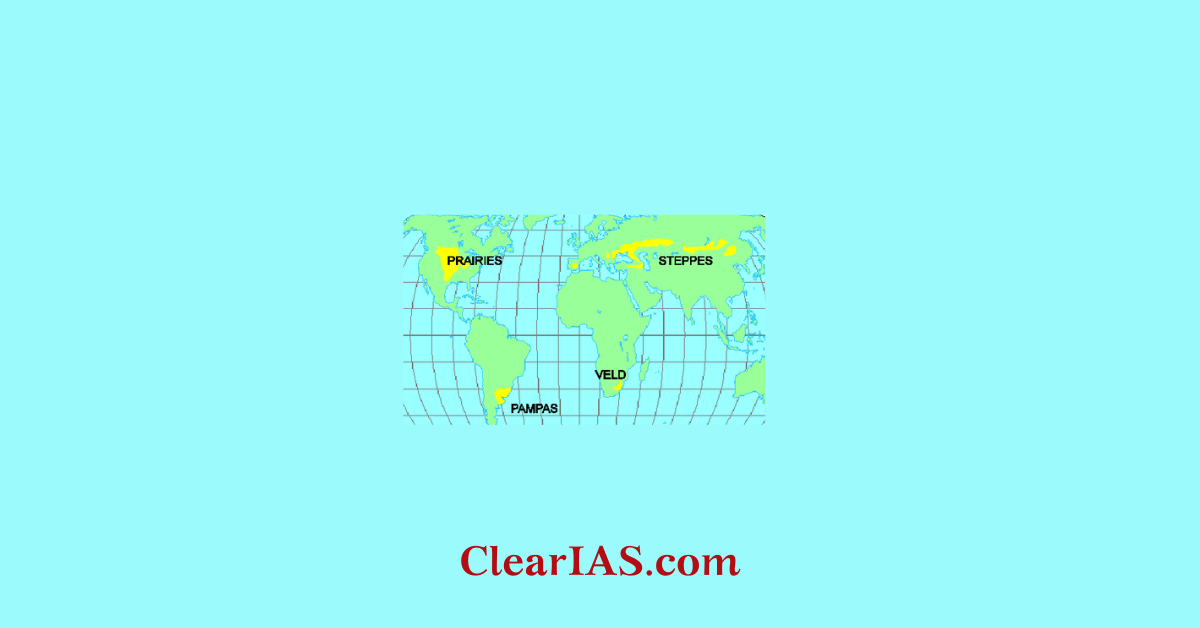
Types of Grasslands:
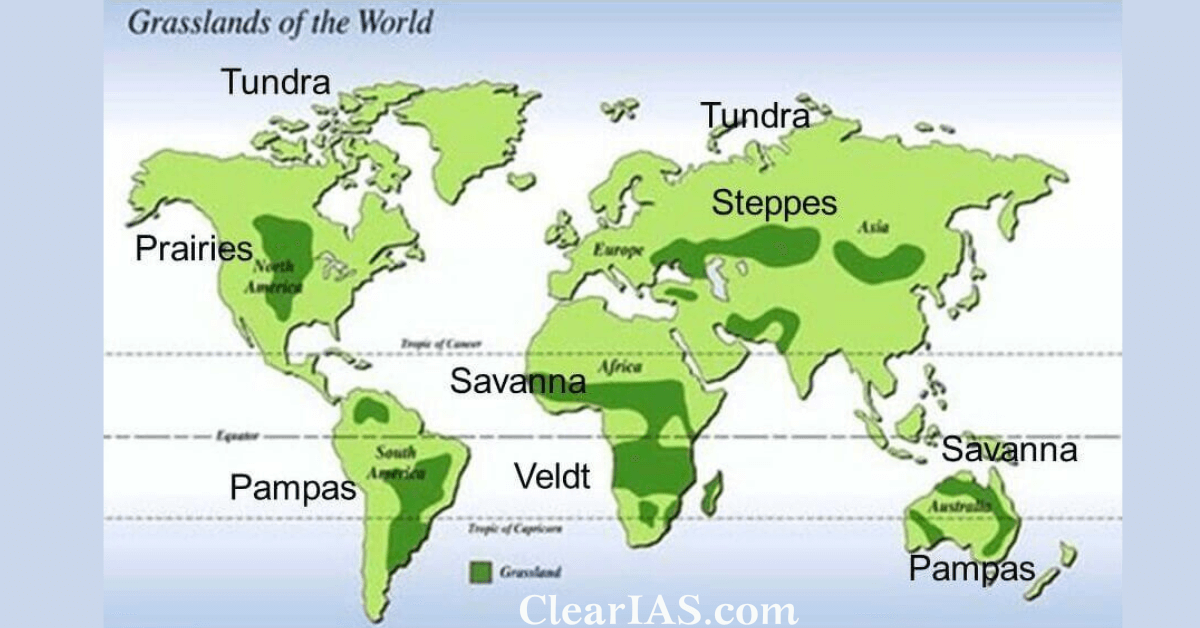
As climate plays an important role in the formation of grasslands, it is generally used as a basis to divide the world’s grasslands into two broad categories: those that occur in the temperate region and those that occur in the tropical regions.
| TROPICAL GRASSLAND | TEMPERATE GRASSLAND |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Economic Activities in different regions
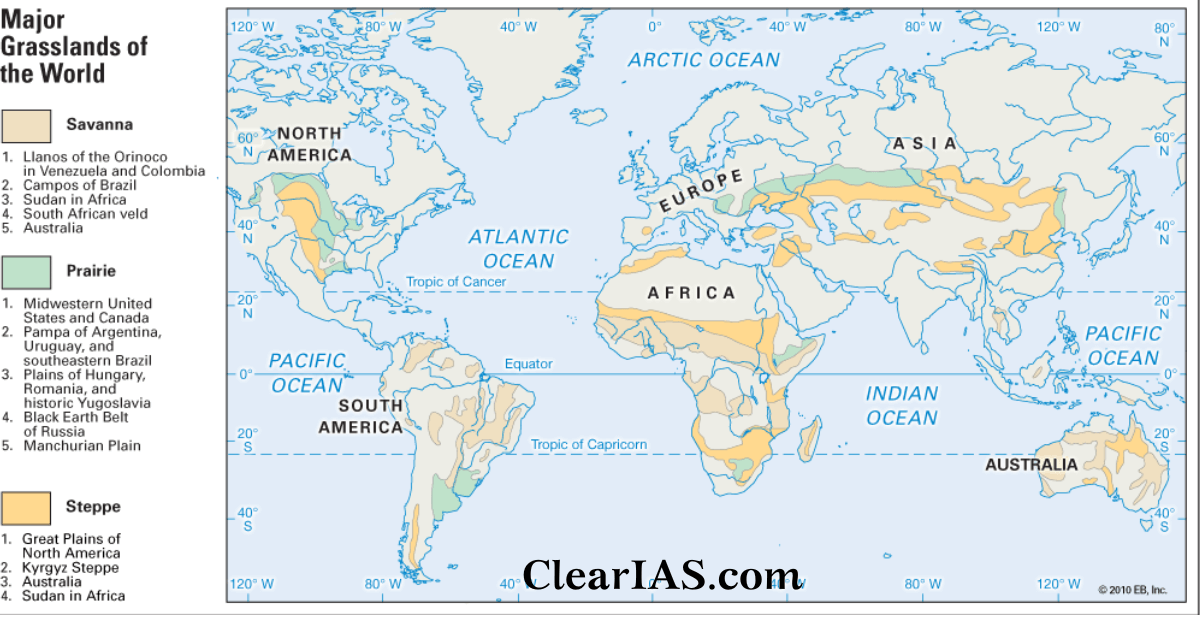
| REGION | GRASSLAND | ECONOMIC ACTIVITIES |
|---|---|---|
| North Asia & Europe | Steppes, Taiga | Major Economic Activities |
| North America | Prairies | Wheat Granaries
Extensive Ranching |
| South America | Pampas, Llanos, Cerrados | |
| Africa | Savannah, Veld | |
| Australia, New Zealand | Downs, Rangeland, Canterbury | Sheep and cattle rearing, Merino sheep: wool production |
| Hungary | Pustaz | Rich black soil
Abundant wheat production Sugar from sugar beet (Beta vulgaris, is a plant whose root contains a high concentration of sucrose) |
| USA | Prairies | |
| Argentina | Pampas | Alfalfa: nutrient-rich grass.
Ranching, cattle rearing, Dairy products Extensive wheat-producing region The economy depends on wheat and beef export |
| South Africa | Veld | Maize farm
Sheep and cattle rearing |
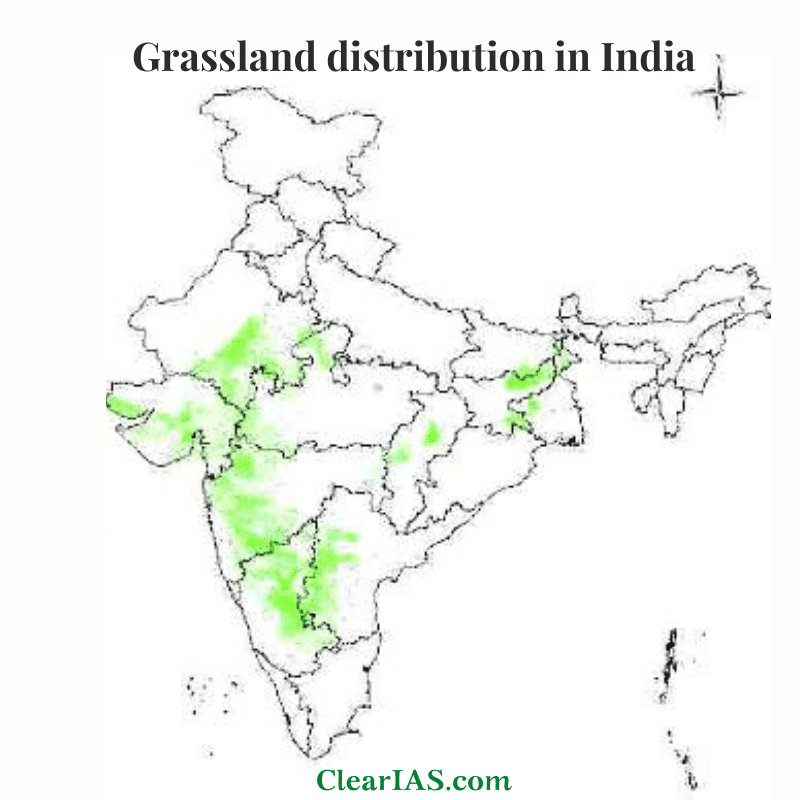
Types of Grasslands In India:
NAME |
SPECIALITY |
REGION |
Semi-arid Zone |
|
|
Dry Sub-Humid Zone |
|
|
Moist Sub Humid Zone |
|
|
Humid Montane Regions |
|
|
In India, grasslands are found as village grazing grounds (Gauchar) and extensive low pastures in dry regions of the western part of the country and also in the Alpine Himalayas. Perennial grasses are the dominant plant community seen here.
In the Himalayan mountains, there are high, cold Himalayan pastures. There are tracts of tall elephant grass in the low-lying Terai belt south of the Himalayan foothills.
There are semi-arid grasslands in Western India, parts of Central India, and the Deccan Plateau. Patches of shola grasslands occur on hill slopes alongside the extremely moist evergreen forests in South India.
Economic Importance of grasslands:
- Wheat, corn, and rice are the three main plants that are grown on grasslands all over the world.
- Farmers who keep cattle or goats, as well as shepherds who keep sheep, are highly dependent on grasslands. It provides a significant food source for cows and sheep.
- Domestic animals are grazed in the ‘common’ land of the village.
- They are the grazing areas of many rural communities.
- Water from semi-natural grasslands is currently in short supply.
- These natural grasslands create an efficient system for water absorption, high infiltration, and reduced erosion.
- Grassland/pasture can sustain plants that honey bees have a long relationship with (clovers and other non-native weeds). Grasslands have diverse species of insects that pollinate crops.
- There are also predators of these insects such as small mammals like shrews, reptiles like lizards, birds of prey, and amphibia such as frogs and toads.
- All these carnivorous animals help to control insect pests in adjoining agricultural lands.
- The grass is also used to thatch houses and farm sheds.
- Grasslands, both natural and semi-natural, play a significant role in the cultural landscape.
- Some grasslands are designated as nature reserves or national parks, and they are frequently promoted as tourist destinations both locally and nationally.
- The thorny bushes and branches of the few trees that are seen in grasslands are used as a major source of fuelwood.
- Locally, however, stakeholders, including regional specialists and local farmers, recognize their importance.
Flora and Fauna of the ecosystem:
- Grasses are the dominating plants, with scattered drought-resistant thorny trees in the tropical grasslands.
- Badgers, foxes, asses, zebra, and antelope are found grazing on grasslands that support the dairy and leather industries.
- Grasslands also support the large population of rodents, reptiles and insects.
- In some regions, grasslands also support a variety of other herbaceous plants like sedges, legumes and members of the sunflower family. Grasslands support numerous herbivores, from minute insects to very large mammals.
- Rats, mice, rodents, deer, elephants, dogs, buffalo, tigers, lions, and ferrets are some common mammals in grasslands.
- In northeast India, the one-horned rhinoceros is among the threatened animal of grassland in this region.
- A large number of avian fauna seen
Characteristics features of this ecosystem:
- Short plants: Grasslands normally have a very short growing season as the climate is dry and the soil is poor. This condition inhibits the growth of woody and large trees and favours the growth of small plants like grass and shrubs.
- Fast-growing grass: Grasses have a tendency to grow back in spite of grazing or overgrazing. Moreover, most grass species can grow quickly after a fire has swept through the grassland and some have seeds that can grow after being burned in a fire.
- Mostly hot and Dry Areas: Nearly all large grasslands are hot, at least in summer and dry. In general tropical grasslands receive 500 to 1500 mm of about 15 to 35 degrees.
- Change in appearance: These ecosystems change their appearance throughout the year. While in winter grasslands look drab and lifeless. A similar change can be seen in tropical grasslands where the onset of the rainy season changes the landscape from dull brown to bright green.
- Grassland also performs Energy flow through the food chain, Nutrient cycling (biogeochemical cycles).
- Ecological succession or ecosystem development.
- Homeostasis (or cybernetic) or feedback control mechanisms.
- To increase the fertility of the soil and regulate the productivity of the ecosystem.
- To reduce the leaching of minerals due to low rainfall.
Conclusion:
The grasslands are one of the most important landforms. They assist agriculture by providing essential ecosystem services such as water and climate regulation, as well as biogeochemical cycling, carbon storage, cultural, and recreational benefits. They are also the major reservoirs of agricultural gene pools, and many of the crops that enable human life, such as wheat, corn, rice, and millet, originated in these ecosystems. Grasslands are also important habitats for a variety of flora and animals.
Article written by Aseem Muhammed






Leave a Reply