
GSLV launch is a great achievement as it used indigenous developed cryogenic engine. Let’s discuss in this post certain keywords related to Space Technology and ISRO like GSLV D5, Cryogenic Engine, GSAT-14 etc.
Also read: Aditya-L1 Mission
GSLV D5 : The rocket

GSLV D5: GSLV D5 is a rocket (launch vehicle) used to launch the satellite GSAT 14. The rocket engine used in this launch vehicle was a cryogenic one, which uses cryogenic propellants at low temperature.
What’s special about GSLV D5 launch? India already had successfully launched many satellites using launch vehicles in the PSLV and GSLV series. But this was for the first time, India successfully launched a satellite using its indigenous developed cryogenic engine. In the previous missions of GSLV, we were using Russian Technology for cryogenic engines. But now, we have mastered cryogenic technology and have emerged as a major space power.
GSLV is a three-stage launch vehicle with solid, liquid and cryogenic stages. It is designed to inject 2 Ton class of communication satellites to Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO). GSLV-D5 vehicle is configured with its first and second stages similar to the ones flown during earlier GSLV missions. The third stage is the indigenous cryogenic stage.
Propellants used in the three stages of GSLV
- 1 Stage (Strap- Ones) : UH25 & N2O4.
- 1 Stage (Core Stage) : HTPB.
- 2 Stage : UH25 & N2O4.
- 3 Stage : LH2 & LOX.
HTPB : Hydroxyl Terminated Poly Butadiene, LH2: Liquid Hydrogen, LOX : Liquid Oxygen.
N2O4 : Nitrogen Tetroxide, UH25 : Unsymmetrical Dimethyl Hydrazine + 25% Hydrazine Hydrate.
Cryogenic propellants used in this mission: liquid oxygen at minus 183 degrees Celsius and liquid hydrogen at minus 253 degrees’ Celsius.
About the cryogenic engine
India’s indigenous cryogenic engine is named CE-7.5. This cryogenic rocket engine is used to power the upper stage of GSLV. The engine was developed as a part of the Cryogenic Upper Stage Project (CUSP). It will replace the KVD-1 (RD-56) currently powering the upper stage of GSLV.
Advantages: Cryogenic rocket stage is more efficient and provides more thrust for every kilogram of propellant it burns compared to solid and earth-storable liquid propellant rocket stages. Specific impulse (a measure of the efficiency) achievable with cryogenic propellants (liquid Hydrogen and liquid Oxygen) is much higher compared to earth storable liquid and solid propellants, giving it a substantial payload advantage. However, cryogenic stage is technically a very complex system compared to solid or earth-storable liquid propellant stages due to its use of propellants at extremely low temperatures and the associated thermal and structural problems.
GSLV Variants:
The main variants are GSLV Mk.I and GSLV Mk.II. GSLV Mk.II variant uses an Indian cryogenic engine, the CE-7.5, and is capable of launching 2500 kg into geostationary transfer orbit. Previous GSLV vehicles (GSLV Mk.I) have used Russian cryogenic engines. GSLV Mk.I had three sub-variants like GSLV Mk.I (a), GSLV Mk.I (b) and GSLV Mk.I (c).
GSAT 14 : The Satellite

After reaching Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO), GSAT-14 will use its own propulsion system to reach its geostationary orbital home and will be stationed at 74º East longitude.
GSAT-14 will help provide many satellite based communication services to the country including tele-education and telemedicine. The satellite carries six Ku-band and six Extended C-band transponders to provide coverage of the whole of India. GSAT-14 also carries two Ka-band beacons which will be used to conduct research into how weather affects Ka-band satellite communications. The satellite is powered by two solar arrays, generating 2,600 watts of power.
PSLV and GSLV
- India had in the last two decades 25 consecutive successes of its Polar Satellite Launch Vehicles (PSLVs).
- GSLV could not claim such a success rate. GSLV has attempted eight launches to date, since its first launch in 2001 through its most recent launch in 2014. Three launches have been successful, four have failed, and one was a partial failure, placing the satellite into an unplanned, but recoverable, orbit.
- While PSLV can carry satellites up to 2 tones to a low earth orbit, GSLV was needed for the launch of heavier satellites, especially of the telecommunication variety that need to be put in a 36,000km geosynchronous orbit.
Perigee and Apogee
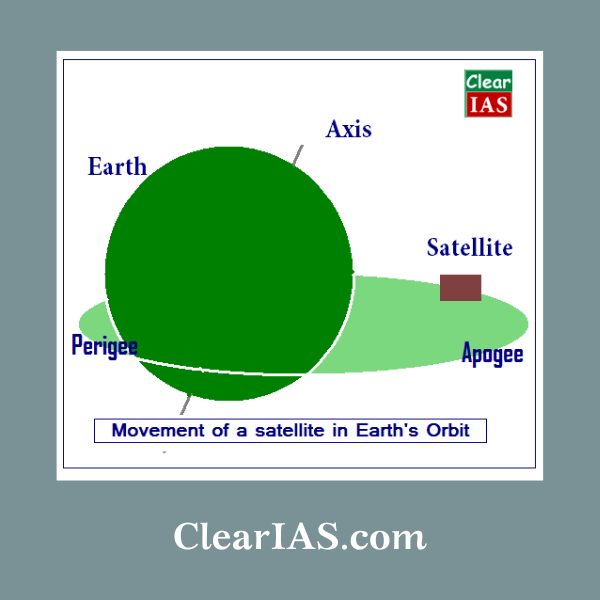 Perigee is the point nearest to earth while Apogee is the farthest point from earth. After a flight of 17 minutes 5 seconds, GSAT-14 satellite was precisely injected into a Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit with a Perigee (nearest point to Earth) of 175 km and an Apogee (farthest point to Earth) of 35,945 km with an orbital inclination of 19.3 degree with respect to the equator.
Perigee is the point nearest to earth while Apogee is the farthest point from earth. After a flight of 17 minutes 5 seconds, GSAT-14 satellite was precisely injected into a Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit with a Perigee (nearest point to Earth) of 175 km and an Apogee (farthest point to Earth) of 35,945 km with an orbital inclination of 19.3 degree with respect to the equator.
Targeted Orbit of GSLV-D5
- Perigee : 180 ± 5 km
- Apogee : 35975 ± 675 km
- Inclination : 19.3 ± 0.1 deg
Mock questions to test your grasp
Qn 1 : Which among the following statements are true regarding India’s space technology?
- GSAT and PSLV are the main rocket launching vehicles of India.
- Satellite launching center of India is at Wheeler Islands, Odisha.
- India’s indigenous cryogenic engine is named Cryo 2014.
Answer Choices :
- A: 1 only.
- B: 2 and 3 only.
- C: All the above.
- D: None of the above.
Qn 2: Which among the following statements is true?
- The Perigee of a satellite corresponds to the farthest point from Earth in its orbit.
- Before placing GSAT 14 into the final Geosynchronous orbit, it was first placed into the Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO)
- India’s indigenous cryogenic engine used for GSAT 14 launch, used liquid Hydrogen and Oxygen in its cryogenic stage.
- GSLV D5 had 4 stages.
- GSAT 14 carried Ku band transponders as well as C band transponders.
Answer Choices :
- A: 1 only.
- B: 2 and 3 only.
- C: 2, 3, and 5 only.
- D: 1, 3, and 5 only.






I liked the article. Everything has been explained in a clear & concise manner.
I liked the idea of introducing questions at the end, however, it may be even more benefitting if the answers are also provided at the same page. Just a minor suggestion. Really good work though.
thank you 🙂
Very good article.Pictorial representations give us a clear idea about the concepts.Good work.Surely your article will help all civil service aspirants.Thank you!!!!
Thank you
both question answer is (c)
no because “The satellite carries six ku-band and six Extended C-band transponders to provide coverage of the whole of India.” so there is no mentioning of 6 ku band and 6 extended c band
Very Informative
THANK YOU SIR
good article…. it helpfull to clear concept…
thanku.
1)D & 2)C….
If i study for mains exam from dis notes it’s enough or wat