Vertical Farming is a concept crucial for sustainable agriculture and for utilizing lesser available arable lands. Read here to know more.
Indian agriculture is evolving every day towards sustainable farming practices. With increasing industrialization and population, the availability of arable lands for agriculture is getting lesser.
In such a situation, new and innovative farming practices are to be used such as zero budget natural farming and vertical farming which have been gaining popularity in the past decade.
Gilbert Ellis Bailey coined the term vertical farming in 1915 and also wrote a book of the same name.
The modern concept was first proposed in 1999 by Professor Dickson Despommier which was centered on the idea that urban areas should grow their food which can save time and resources required for transportation.
What is vertical farming?
In vertical farming, crops are grown indoors, under artificial conditions of light and temperature. It aims at higher productivity in smaller spaces.
Vertical farming is conceptualized as cultivating and producing crops or plants in vertically stacked layers and vertically inclined surfaces.
It uses soil-less methods such as hydroponics, aquaponics, and aeroponics.
Vertical farming uses significantly less water and pesticides than traditional agricultural methods.
Being indoors, the crops aren’t subject to seasons and hence give high productivity year-round.
Lettuces, tomatoes, and green crops can be produced through this practice.
Japan has been one of the early pioneers in vertical farming. It holds the largest share in the global vertical farming market. In Japan, vertical farming is born out of necessity whereas traditional farming is losing its face due to the aging population and rural migration.
Vertical farming systems come under the broad classification of protected cultivation wherein the variable physical parameters like temperature, water, soil, humidity, etc can be regulated.
Advantages and disadvantages of vertical farming
Vertical Farming has several advantages, which make it promising for the future of agriculture.
- The land requirement is quite low, water consumption is 80 percent less, the water is recycled and saved, it is pesticide-free, and in cases of high-tech farms, there is no real dependency on the weather.
- A vertical farm can be set up within the confines of a city.
- And when the farms are nearby, the product is quickly delivered and always fresh; when compared to the refrigerated produce usually available at supermarkets.
- Reduction in transportation reduces the fossil fuel cost & resulting emissions and thus also reduce the spoilage in transportation.
However, vertical farming has its drawbacks.
- Initial capital costs for establishing the vertical farming system are the major problem.
- In addition, there are costs of erecting the structures along with its automation like computerized and monitoring systems, remote control systems and software, automated racking and stacking systems, programmable LED lighting systems, climate control system, etc.
Types of vertical farming
There are three major soil-less methods of vertical farming- hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics.
Hydroponics
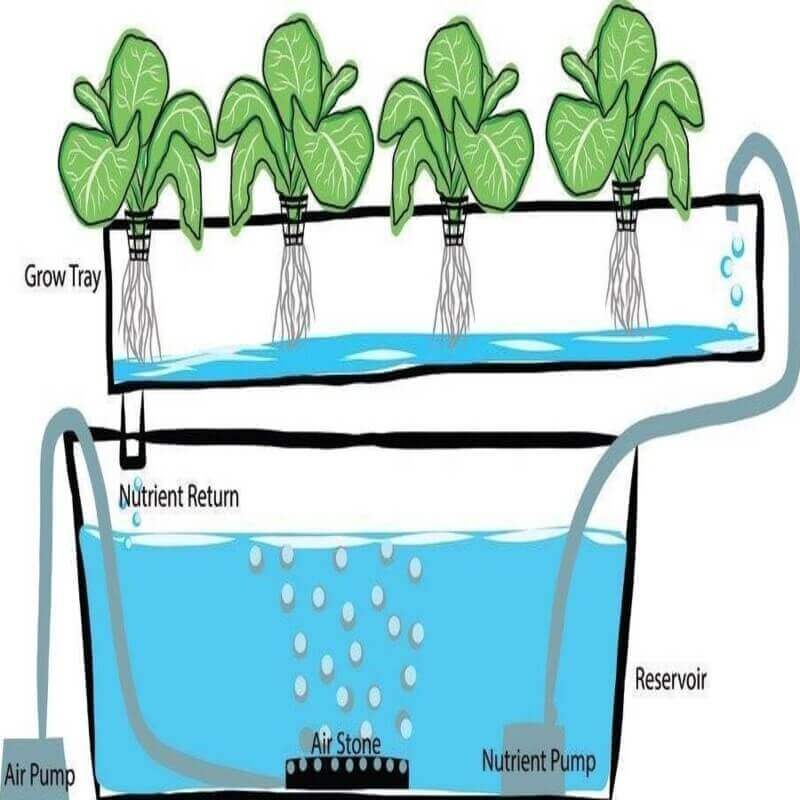
In the early 1930s, William Frederick Gerick pioneered hydroponics at the University of California at Berkley.
It is a method of growing food in water using mineral nutrient solutions without soil.
The basic advantage of this method is that it reduces soil-related cultivation problems like soil-borne insects, pests, and diseases.
A hydroponics system eliminates the need for soil by providing a nutrient-charged aqueous solution directly to the roots that keep the plant fed and hydrated, while supplemental lighting solutions mimic sunlight.
In a hydroponics growing system, plants are either suspended directly in the aqueous solution or grown in a soil-free medium such as coconut coir, rock wool, LECA, vermiculite, or perlite. The plant’s roots receive the nutrient solution in either an active system or a passive system.
- Active systems use pumps to circulate and aerate nutrient solutions, delivering the nutrients to the plant’s root zone for uptake.
- Passive systems have no pumps or moving parts. The nutrient solutions are fed to the root zone through flooding, gravity, or capillary action.
Advantages:
- An extended growing season
- Improved growth and yield
- Higher plant density
- Plants can grow anywhere
- Less water consumption
- Fewer pest problems
- Easier to harvest mature plants
Disadvantages:
- Expensive to set up compared to traditional gardening methods
- Vulnerable to power outages due to dependence on electricity for light, water pump, aerators, etc.
- Requires constant monitoring and maintenance.
- Vulnerable to waterborne diseases
- Without soil as a buffer, plants get negatively affected by physical changes quicker.
Aeroponics
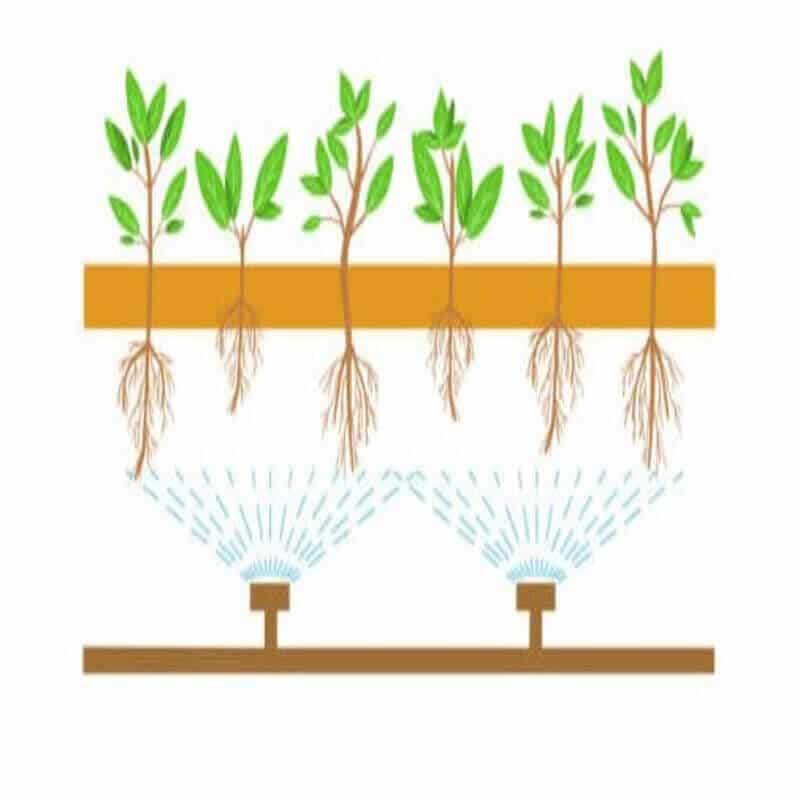
The invention of aeroponics was motivated by the initiative of NASA (the National Aeronautical and Space Administration, USA) to find an efficient way to grow plants in space in the 1990s.
In aeroponics, there is no growing medium and hence, no containers for growing crops. In aeroponics, mist or nutrient solutions are used instead of water. As the plants are tied to support and roots are sprayed with nutrient solution, it requires very less space, very less water, and no soil.
Compared to regular hydroponic plants, the plants tend to grow faster and absorb more nutrients because the roots are exposed to more oxygen. Also, there are fewer threats of diseases around root zone disease because there’s no place for debris or pathogen to reside.
Advantages:
- Maximum nutrient absorption for plant roots due to no growing medium
- Massive plant growth because plant roots are exposed to oxygen 24/7. This promotes healthy and fast-growing plants. The mist used on the roots can also be sterilized to prevent plant diseases.
- Higher yields in smaller spaces.
- Considerably fewer nutrients and water are used on average compared to other systems because of the higher nutrient absorption rate.
- Mobility- plants can be moved around easily.
- Easy system maintenance because there is no growing medium used and the system can be cleaned easily
Disadvantages:
- Requires constant attention to pH and nutrient density ratio because this system is sensitive.
- The cost for initial setup can be high.
- Susceptible to power outages.
- Require technical knowledge as it is one of the most technical to set up.
- Dependence on the system. An aeroponic system is made of mist nozzles, high-pressure pumps, and a timer.
- Require regular disinfection of the root chamber (a common disinfectant is hydrogen peroxide) to prevent root diseases.
- Microorganisms can be introduced to plant roots through the water.
Aquaponics
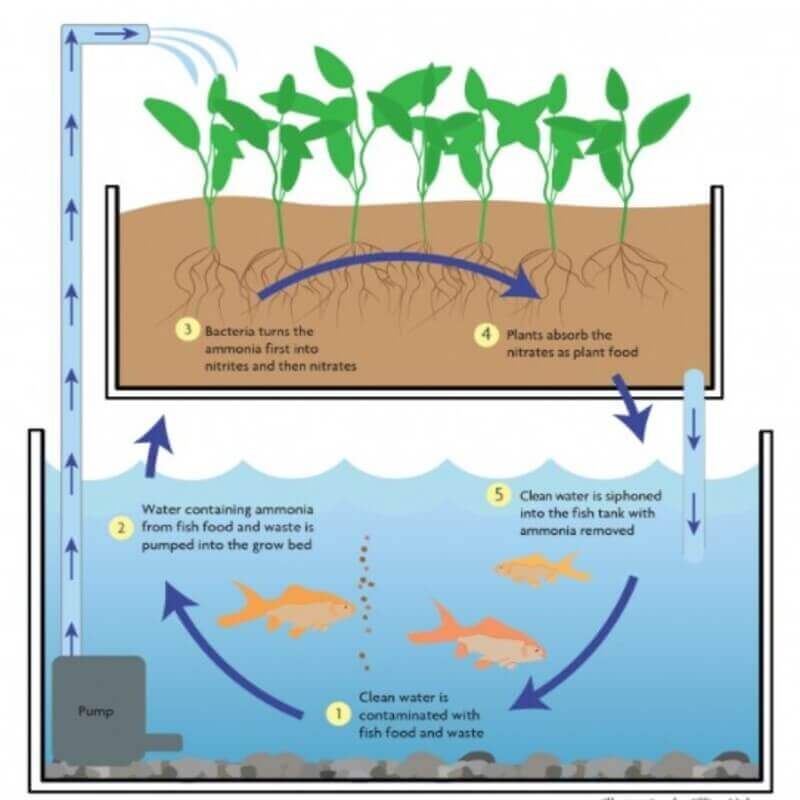
The term aquaponics is coined by combining two words: aquaculture, which refers to fish farming, and hydroponics the technique of growing plants without soil, to create symbiotic relationships between the plants and the fish.
The symbiosis is achieved as nutrient-rich waste from fish tanks serves as “fertigate” to hydroponic production beds. In turn, the hydroponic beds also function as bio-filters that remove gases, acids, and chemicals, such as ammonia, nitrates, and phosphates, from the water.
Advantages:
- Sustainable and intensive food production system sustainable;
- Aquaponics is an extremely water-efficient system.
- Doesn’t require soil and therefore it’s not susceptible to soil-borne diseases
- Doesn’t require using fertilizers or chemical pesticides;
- Higher yields and qualitative production; higher level of biosecurity and lower risks from outer contaminants;
- Aquaponics can be used on non-arable lands such as deserts, degraded soil, or salty, sandy islands;
- From a nutritional standpoint, aquaponics provides food in the form of both protein (from the fish) and vegetables
Disadvantages:
- The very high initial start-up costs compared with both hydroponics and soil production systems.
- Aquaponics requires deep expertise in the natural world.
- It’s often hard to find a perfect match between the needs (such as pH, temperature, substrate) of fish and plants;
- Aquaponics has fewer management options compared with stand-alone aquaculture or hydroponics;
- Mistakes in managing the system can quickly cause its collapse;
- Daily management is needed and has energy costs;
- Fish feed needs to be purchased regularly;
- The products of aquaponics alone aren’t enough to ensure a balanced diet.
Way forward
Vertical farming practice is still in a nascent stage in India, but it needs to be encouraged more to ensure better food security with the increasing population. It can aid in tackling malnutrition and promises better food distribution.
A variety of stakeholders from household farmers and small- to large-scale farmers can be taught the specific knowledge and skills needed for safe, successful, and sustainable implementation.
With vertical farming techniques, the discussions around farming can move away from land constraints to focus more on sustainable farming techniques.
The science of different vertical farming techniques can be taught at the school level itself, hence developing sustainable practitioners at a young age itself.






Leave a Reply